beta arrestin pathway|GPCR signaling via β : Baguio The two β-arrestins, β-arrestin-1 and -2 (systematic names: arrestin-2 and -3, respectively), are multifunctional intracellular proteins that regulate the activity of a very large number of cellular signaling pathways and physiologic functions. 1: 2: 2 bets on 1 selection. One to win and one to place. Double: 2: 1: 1 bet on 2 selections. Treble: 3: 1: 1 bet on 3 selections. Accumulator: 4+ 1: 1 bet on up to 20 selections. Trixie: 3: 4: 3 doubles, 1 treble. Patent: 3: 7: 3 singles, 3 doubles, 1 treble. Yankee: 4: 11: 6 doubles, 4 trebles, 1 four-fold accumulator. Canadian: 5: 26: 10 .In many ways, the modern 5d lottery or Khmer lottery 5d is comparable to the game of 4D. The primary distinction, as implied by the name, is the quantity of numbers from which to choose. With modern lottery 5d results, you must select five numbers of your choosing. It is entirely up to you to select alternative numbers of repeats.
beta arrestin pathway,
In this review, we summarize various signaling pathways mediated by β-arrestins and highlight the physiologic effects of β-arrestin-dependent signaling. Keywords: Arrestin, endocytosis, 7TMR, adaptor, GPCR, biased agonist, kinase.
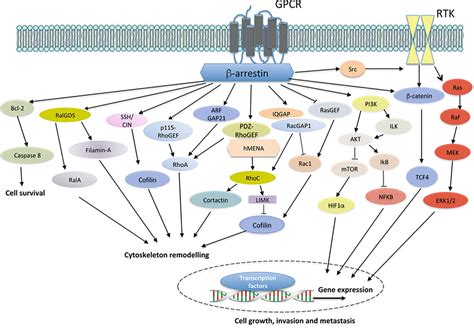
The two β-arrestins, β-arrestin-1 and -2 (systematic names: arrestin-2 and -3, respectively), are multifunctional intracellular proteins that regulate the activity of a very large number of cellular signaling pathways and physiologic functions.
β-arrestins interact with hundreds of GPCRs and participate in various signaling pathways to carry out their diverse cellular functions. These GPCRs include but are not limited to adrenergic,.

β-Arrestins 1 and 2 couple to seven trans-membrane receptors and regulate G protein-dependent signaling, receptor endocytosis and ubiquitylation.β-Arrestins 1 and 2 couple to seven trans-membrane receptors and regulate G protein-dependent signaling, receptor endocytosis and ubiquitylation.

By serving as multiprotein scaffolds, the beta-arrestins bring elements of specific signaling pathways into close proximity. beta-Arrestin regulation has been demonstrated for an ever-increasing number of signaling molecules, including the mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK, JNK, and p38 as well as Akt, PI3 kinase, and RhoA.beta arrestin pathway Perhaps one of the best characterized arrestin pathway-selective biased agonist is that mediated through the type 1 human parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R). The PTH1 receptor regulates calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism.
beta arrestin pathway GPCR signaling via β Perhaps one of the best characterized arrestin pathway-selective biased agonist is that mediated through the type 1 human parathyroid hormone receptor (PTH1R). The PTH1 receptor regulates calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism.GPCR signaling via β Activation of δ-opioid receptors leads to the β-arrestin-1-dependent increase in p27 transcription and inhibition of growth of human neuroblastoma cells, which underlines the physiological significance of this β-arrestin-mediated epigenetic regulatory pathway.
GPCRs convert stimuli from the extracellular to the cytoplasm through two classical signaling pathways, the G protein dependent pathway and the β-arrestin (βarr) dependent pathway. These.
beta arrestin pathway|GPCR signaling via β
PH0 · β−Arrestins: Structure, Function, Physiology, and
PH1 · β
PH2 · The multifaceted functions of β
PH3 · New Roles for β
PH4 · GPCR signaling via β
PH5 · Dynamic mechanism of GPCR
PH6 · Classical and new roles of β
PH7 · Beta